Zero Trust - Foundational Cyber-Security
In any threat-laden digital environment, adopting a robust security framework to protect your assets is a necessity. Zero Trust is a transformative cybersecurity model that eliminates implied trust and requires continuous verification of every access request.
At its core, Zero Trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," reducing the attack surface and limiting the blast radius in case of breaches.
Microsolve are experts in the design and deployment of Zero Trust environments for your business.
Understanding Zero Trust
Zero Trust is a security model designed to address modern cybersecurity challenges such as distributed workforces, cloud adoption, and IoT proliferation.
Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models that assume trust within the network, Zero Trust assumes no user or device can be trusted by default—whether inside or outside the network perimeter.

Delivering Zero Trust for YOUR Network
By partnering with us, you gain access to cutting-edge cybersecurity expertise that not only protects your assets but also enhances productivity through secure and seamless access controls. We don't just think we know this - we use it ourselves!
Transitioning to a Zero Trust model is not just about adopting new technologies; it’s about embracing a new mindset focused on proactive defense starting with network architecture and design.
With our expertise in deploying solutions using providers such as Cisco, Fortinet, Extreme, Azure and AWS and our commitment to "verify always," we help you reduce your attack surface while limiting the blast radius of potential threats—ensuring your organisation's resilience to the current threat landscape.
Zero Trust - The Core Principles
- Verify Always: Continuous verification of users and devices is mandatory for every access request. This includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), identity verification, and endpoint validation.
- Least Privilege Access: Users and devices are granted only the minimum access required to perform their tasks, reducing unnecessary exposure to sensitive resources.
- Limit the Blast Radius: Through micro-segmentation (VLANs and VRF's) and identity-based policies, Zero Trust minimizes lateral movement within the network. This ensures that if a breach occurs, its impact is contained.
- Dynamic Context-Aware Policies: Access decisions are based on contextual factors like user behavior, device health, location, and time of access.
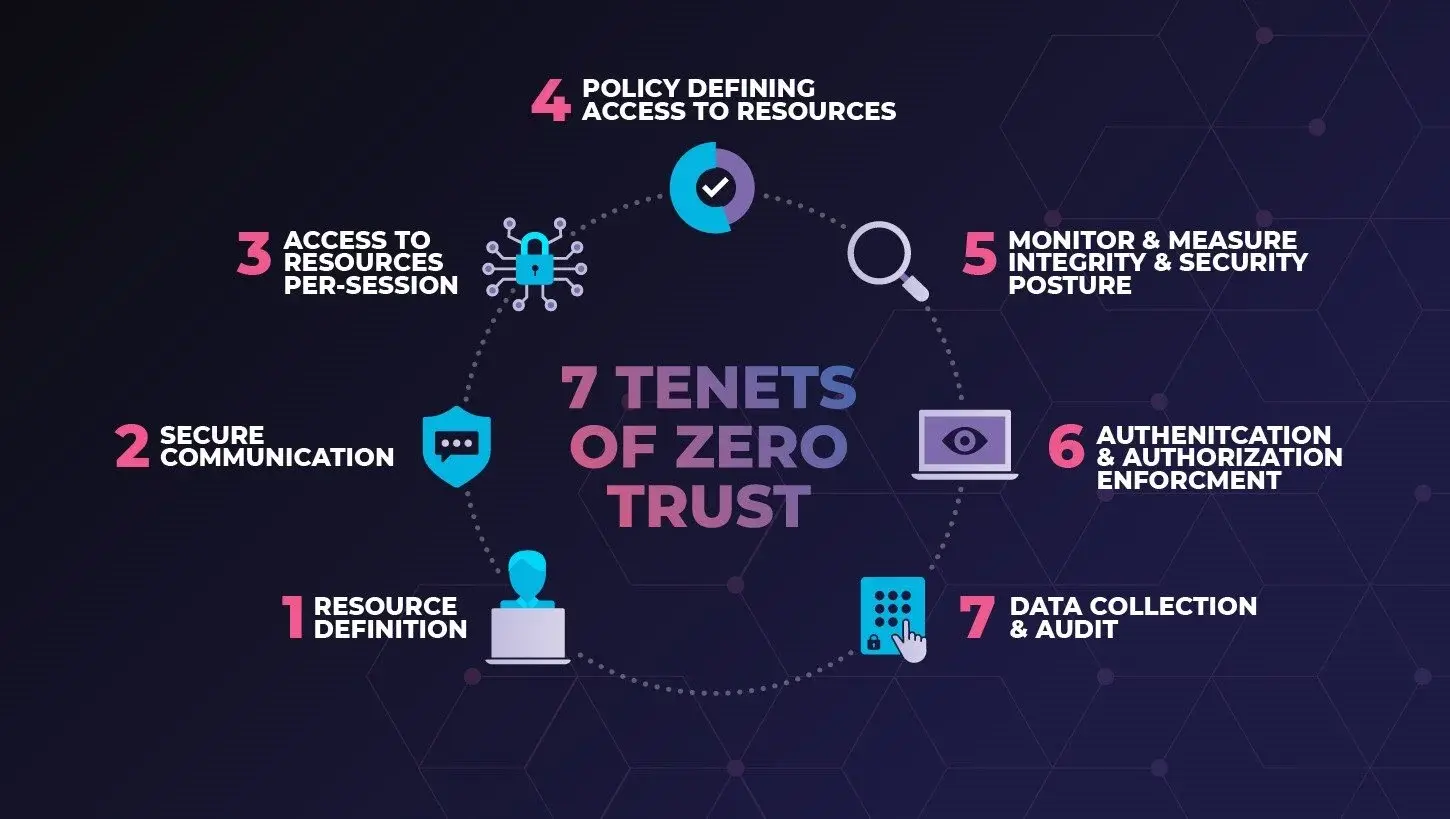
The Microsolve Approach to Zero Trust Deployment
As an MSP with significant experience in Zero Trust deployments, we guide organisations through a structured implementation process tailored to their unique needs.
Leveraging Vendor guides with internally developed processes and architecture statements, Microsolve will ensure that your Zero Trust deployment is seamlessly integrated with your existing IT infrastructure.
1. Define the Attack Surface
The first step in deploying Zero Trust is identifying critical assets, data flows, and vulnerabilities within the network. This includes mapping out applications, devices, users, and workflows.
2. Architect a Zero Trust Network
Using solutions such as FortiGate firewalls and FortiClient EMS (Endpoint Management Server), organizations can implement ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access). This architecture replaces traditional VPNs with secure, role-based access to applications—whether on-premises or in the cloud.
3. Enforce Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation divides the broader network into smaller segments with strict access controls at each layer - using service based VLAN's, VRF's and identity based service mapping techniques are supported by network vendors such as Cisco, Fortinet and Extreme.
4. Implement Continuous Verification
Fortinet's ZTNA framework ensures that every access request is authenticated and authorized dynamically. This includes integrating MFA and endpoint security tools to validate user identity and device compliance.
5. Automate Policy Enforcement
Fortinet's centralized management tools allow MSPs to automate context-aware policy enforcement across hybrid environments. These policies adapt dynamically based on risk levels, ensuring consistent protection without compromising user experience.
6. Selecting the Vendor
Zero Trust FAQ's
Zero Trust is a modern security framework that operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within a network perimeter, Zero Trust continuously verifies users, devices, and access requests.
Zero Trust reduces risks by:
- Minimizing the attack surface: Only authorized users and devices can access specific resources.
- Limiting the blast radius: Through micro-segmentation and least-privilege access, it contains potential breaches to a small area, preventing lateral movement across the network.
- Continuous monitoring: Every access request is verified in real-time, ensuring dynamic threat detection and response.
Traditional security models rely on perimeter-based defenses, assuming that anything inside the network is trustworthy. In contrast, Zero Trust assumes that no user or device can be trusted without verification, regardless of their location. This shift addresses modern challenges like cloud adoption, remote work, and insider threats.
The three main principles are:
- Verify always: Continuously authenticate and authorize every access request.
- Use least privilege access: Grant users and devices only the minimum permissions needed for their tasks.
- Assume breach: Design systems to limit damage in case of a breach by segmenting resources and monitoring activity.
No, Zero Trust is scalable and beneficial for organisations of all sizes. Small businesses can implement foundational elements like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and endpoint security, while larger enterprises may adopt more complex strategies like micro-segmentation and dynamic policy enforcement.
While it may seem counterintuitive, Zero Trust can enhance user experience by:
- Reducing unnecessary access interruptions through risk-based policies.
- Ensuring secure access to applications and data from anywhere without relying on outdated technologies like VPNs.
- Providing seamless authentication processes tailored to user behavior and context.
Deploying Zero Trust typically involves:
- Identifying critical assets and mapping the attack surface.
- Implementing continuous verification mechanisms like MFA.
- Enforcing least privilege access policies.
- Segmenting networks to contain potential breaches.
- Monitoring user behavior and automating threat responses.
Although implementation can be complex, starting with incremental changes ensures steady progress toward a more secure environment.

